Arthritis: Understanding the Condition and Its Management
Arthritis is a common global health issue that affects millions of people. It is a broad term that encompasses various conditions that cause inflammation and damage to the joints. The purpose of this article is to provide an in-depth understanding of arthritis, including its types, symptoms, causes, diagnosis methods, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Types of Arthritis
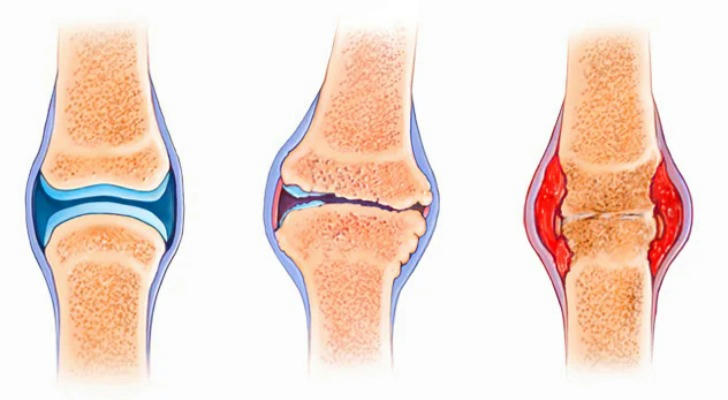
- Osteoarthritis: This is the most common form of arthritis, often referred to as wear-and-tear arthritis. It occurs when the protective cartilage at the ends of the bones wears down over time.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This is an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing chronic inflammation.
- Gout: This type of arthritis is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and severe attacks of pain and swelling.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Arthritis patients usually experience a series of symptoms, mainly including joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. In addition, there may be limited range of motion, reduced flexibility, cracking or grating sounds in the joints, as well as fatigue and general discomfort.
Causes of Arthritis
- Age factor: The risk of developing arthritis increases gradually with age.
- Injury factor: Previous joint injuries can increase the likelihood of developing arthritis later in life.
- Genetic factor: Some forms of arthritis are closely related to genetic factors.
- Obesity factor: Excessive weight places additional stress on the joints, thereby increasing the risk of arthritis.
Diagnosis of Arthritis
For the diagnosis of arthritis, a series of examinations are usually required, including physical examination, imaging tests (such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound), and blood tests. These examinations can help doctors understand the condition of the joints, determine whether there is inflammation and the degree of inflammation, etc.
Treatment Options for Arthritis
- Medications: Including anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologics. These drugs can effectively relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and control the development of the disease.
- Physical therapy: Through physical therapy, such as exercise training, heat therapy, and cold therapy, it can improve the flexibility and stability of the joints, enhance muscle strength, and relieve pain.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapists can help patients adapt to activities in daily life, provide assistive devices and guidance to improve the quality of life.
- Surgery: In severe cases, such as when the joints are severely damaged or lose their function, joint replacement surgery may be necessary.
Preventive Measures for Arthritis
- Maintain a healthy weight: By maintaining a healthy diet and moderate exercise, the burden on the joints can be reduced.
- Regular exercise: Appropriate exercise can enhance the flexibility and stability of the joints and prevent the occurrence of arthritis.
- Avoid repetitive stress: Avoid long-term repetitive actions to reduce the risk of joint damage.
- Protect joints: When engaging in sports or daily activities, pay attention to protecting the joints to avoid injury.
A Real Case of Preventing Arthritis
John is a 60-year-old American. He has always been very concerned about his health and has taken various preventive measures to avoid arthritis. He maintains a balanced diet, including plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. He also makes sure to get enough calcium and vitamin D through food or supplements.
In addition, John keeps active. He goes for walks, swims, and does light exercises regularly. He avoids sitting for long periods and takes breaks to stretch his body. He also pays attention to protecting his joints, wearing proper shoes and using assistive devices when needed.
Thanks to his efforts, John has managed to keep his joints healthy and has avoided the development of arthritis so far.
Conclusion
Arthritis is a significant health concern, but through in-depth understanding and scientific management, its impact can be effectively minimized. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle adjustments are all very important. If joint symptoms occur, it is necessary to seek medical advice in time to obtain timely diagnosis and treatment. At the same time, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and a positive attitude is also crucial for coping with arthritis.
